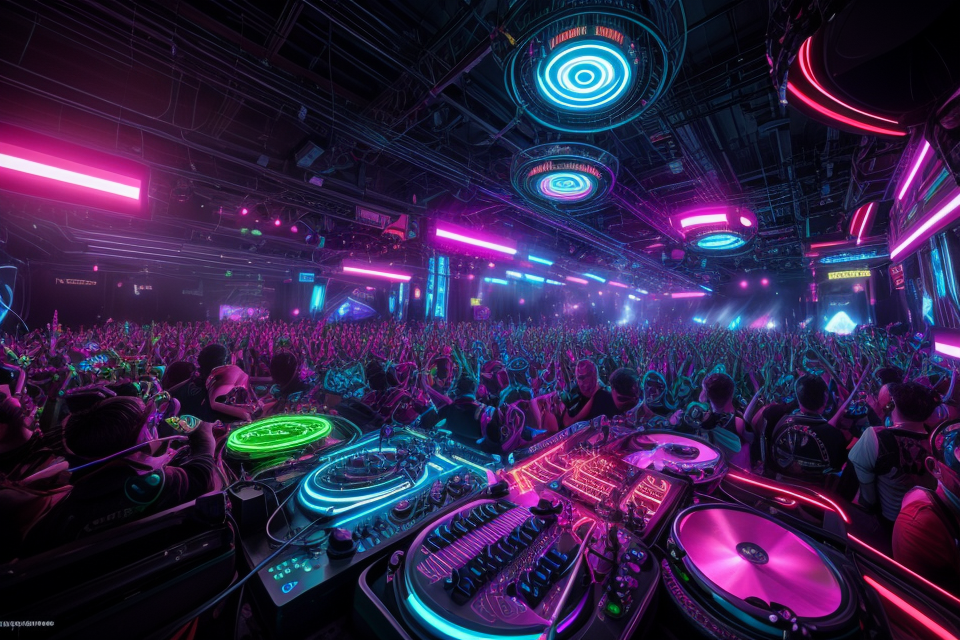
Electronic Dance Music (EDM) has taken the world by storm, with its thumping beats and infectious rhythms. But have you ever wondered about the instruments used in creating these electrifying tunes? From synthesizers to drum machines, the world of EDM is full of unique and innovative instruments that bring the music to life. In this guide, we will explore the fascinating world of EDM instruments, discovering the tools and techniques used by the genre’s top producers to create some of the most iconic sounds in modern music. So, get ready to immerse yourself in the world of EDM and discover the instruments that bring the beats to life!
The Origins of Electronic Dance Music
The Emergence of Electronic Instruments
Electronic Dance Music (EDM) has its roots in the 1960s and 1970s, when musicians and engineers began experimenting with electronic instruments and recording technology. This new technology allowed for the creation of a wide range of sounds that were previously impossible to produce with traditional instruments.
One of the earliest electronic instruments was the theremin, which was invented in the 1920s by Leon Theremin. The theremin is an early electronic instrument that is played without any physical contact by the performer. It works by detecting the position of the performer’s hands and then generating a corresponding sound. The theremin was used in a number of early electronic music compositions, but it was not until the 1960s and 1970s that it became more widely used in popular music.
Another important electronic instrument that emerged in the 1960s was the synthesizer. The synthesizer is an electronic instrument that generates a wide range of sounds by combining different waveforms and filtering them through various electronic circuits. The first synthesizers were large and expensive, but they quickly became popular among musicians and producers because of their ability to create new and unique sounds.
The 1970s saw the emergence of the drum machine, which allowed musicians to create rhythms and beats electronically. This was a significant development for EDM, as it allowed for the creation of repetitive and complex rhythms that were not possible with traditional drumming techniques.
The 1980s saw the widespread adoption of digital technology in music production, which led to the development of new instruments such as the sampler and the sequencer. These instruments allowed for the creation of complex and layered sounds, and they became essential tools for many EDM producers.
Today, electronic instruments play a central role in the production of EDM, and there are countless different types of instruments available to producers and musicians. From digital synthesizers to virtual instruments, there is a vast array of tools available for creating the complex and layered sounds that are the hallmark of EDM.
The Evolution of Synthesizers
The evolution of synthesizers can be traced back to the early 20th century when electronic music pioneers began experimenting with various electronic devices to create new sounds. The first electronic instruments were created in the 1920s, but it wasn’t until the 1960s that synthesizers as we know them today began to emerge.
One of the earliest and most influential synthesizers was the RCA Mark II, which was developed in the 1950s by the Radio Corporation of America (RCA). This synthesizer used vacuum tubes to generate sound and was capable of producing a wide range of timbres and textures.
In the 1960s, synthesizers became more portable and affordable, making them accessible to a wider range of musicians and artists. The Moog synthesizer, developed by Robert Moog in the late 1960s, was one of the most popular synthesizers of this era and remains a beloved instrument to this day.
Throughout the 1970s and 1980s, synthesizers continued to evolve and became an integral part of many genres of music, including disco, punk, and new wave. In the 1990s and 2000s, digital synthesizers became popular, offering even more versatility and flexibility than their analog counterparts.
Today, synthesizers continue to play a crucial role in the world of electronic dance music, with new technologies and innovations constantly emerging. From vintage analog synthesizers to cutting-edge digital instruments, there is a wide range of tools available to producers and musicians looking to create unique and captivating sounds.
Types of Electronic Instruments Used in EDM
Synthesizers
Synthesizers are electronic instruments that generate sound by creating and manipulating electrical signals. They are used extensively in electronic dance music (EDM) to create a wide range of sounds, from simple tones to complex textures.
There are several types of synthesizers used in EDM, including:
- Analog synthesizers: These synthesizers use analog circuits to generate sound. They are known for their ability to create rich, complex sounds and are often used in genres such as techno and house.
- Digital synthesizers: These synthesizers use digital signal processing (DSP) algorithms to generate sound. They are known for their ability to create precise, accurate sounds and are often used in genres such as trance and hardstep.
- Hybrid synthesizers: These synthesizers combine elements of both analog and digital synthesis to create unique sounds. They are known for their versatility and are often used in genres such as dubstep and electro.
Each type of synthesizer has its own unique characteristics and can be used to create a wide range of sounds. For example, analog synthesizers are often used to create warm, fat, and analog-sounding leads, while digital synthesizers are often used to create precise, digital-sounding sounds such as plucks and blips.
Hybrid synthesizers, on the other hand, are known for their ability to combine the warmth of analog synthesis with the precision of digital synthesis. They are often used to create complex, evolving sounds and textures.
In conclusion, synthesizers are a crucial part of the EDM production process and are used to create a wide range of sounds. From simple tones to complex textures, synthesizers are the backbone of EDM and allow producers to create unique and original sounds.
Drum Machines
Drum machines are electronic instruments that are designed to imitate the sound of drums and percussion. They are a fundamental component of electronic dance music (EDM) and are used to create the rhythmic foundation of many genres, including techno, house, and electro.
Drum machines come in a variety of shapes and sizes, ranging from small, portable devices to large, complex systems. They typically consist of a keyboard or pad-based interface that allows the user to input drum patterns and sounds. Some drum machines also feature built-in effects, such as reverb and delay, which can be used to enhance the overall sound of the instrument.
One of the key advantages of drum machines is their versatility. They can be used to create a wide range of drum sounds, from the classic, mechanical sounds of early drum machines to more modern, digital sounds that incorporate elements of other instruments, such as synthesizers and samplers. This versatility allows EDM producers to create a wide range of rhythmic textures and patterns, from simple, four-on-the-floor beats to complex, polyrhythmic grooves.
In addition to their musical uses, drum machines also have a number of practical applications. They can be used to create click tracks for live performances, or to provide a steady rhythmic foundation for other instruments and sounds. They can also be used to generate sound effects, such as gunshots or explosions, for use in film and television production.
Despite their widespread use in EDM, drum machines have not always been embraced by all music makers. In the early days of electronic music, many musicians and producers viewed drum machines as cold and mechanical, preferring the more organic sounds of acoustic drums. However, as technology has advanced and the sounds of drum machines have become more sophisticated, they have become an essential tool for many EDM producers.
Today, drum machines continue to play a central role in the world of EDM. They are used to create the rhythmic foundation of many genres, and are often combined with other electronic instruments, such as synthesizers and samplers, to create complex, multilayered sounds. Whether used for their musical or practical applications, drum machines remain an essential tool for many EDM producers.
Samplers
Samplers are electronic instruments that allow users to manipulate and replay recorded sounds. They work by digitizing sound waves and storing them as data that can be accessed and played back through the sampler. Samplers have become an essential tool in the world of electronic dance music, as they provide producers with a vast array of sounds to incorporate into their productions.
There are two main types of samplers: hardware and software. Hardware samplers are physical devices that can be connected to a computer or audio interface, while software samplers are digital programs that run on a computer or mobile device. Both types of samplers have their own unique advantages and disadvantages, and producers often use a combination of both to create their music.
Hardware samplers offer a tactile and immediate experience, with physical controls that allow for quick and easy sound manipulation. They also tend to have a higher-quality sound and better reliability than software samplers. However, hardware samplers can be expensive and may not offer the same level of flexibility as software samplers.
Software samplers, on the other hand, offer a more affordable and versatile option, with a wide range of features and capabilities. They can be used on a computer or mobile device, and offer the ability to edit and manipulate sounds in real-time. Software samplers also tend to offer a larger library of sounds, with the ability to download additional sound packs to expand the library.
In addition to hardware and software samplers, there are also various types of sampler instruments, such as virtual instruments and sample-based instruments. Virtual instruments are software programs that simulate the sound of traditional instruments, such as pianos, guitars, and drums. Sample-based instruments, on the other hand, use pre-recorded sounds and allow producers to manipulate and layer them to create new sounds.
Overall, samplers are an essential tool in the world of electronic dance music, providing producers with a vast array of sounds to incorporate into their productions. Whether using hardware or software samplers, or a combination of both, producers can create unique and dynamic sounds that capture the essence of electronic dance music.
Sequencers
A sequencer is an electronic instrument that is used to create and manipulate sequential patterns of musical notes and sounds. It is one of the most fundamental and essential tools in the world of electronic dance music (EDM). Sequencers can be used to create a wide range of musical styles, from techno and house to trance and dubstep.
One of the key features of a sequencer is its ability to store and play back pre-recorded musical patterns. These patterns can be edited and manipulated in real-time, allowing the user to create complex and intricate musical arrangements. Sequencers can also be used to control other electronic instruments, such as synthesizers and drum machines, making them an essential tool for many EDM producers.
There are several different types of sequencers available, each with its own unique features and capabilities. Some of the most popular types of sequencers include:
- Step sequencers: These sequencers allow the user to enter notes and sounds one at a time, creating a sequence of steps that can be played back in a variety of ways.
- Real-time sequencers: These sequencers allow the user to enter notes and sounds in real-time, creating a sequence of sounds that can be played back immediately.
- Pattern-based sequencers: These sequencers allow the user to create and save patterns of notes and sounds, which can be recalled and played back at any time.
Regardless of the type of sequencer used, they all have one thing in common: they allow EDM producers to create complex and intricate musical arrangements with ease. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced producer, a sequencer is an essential tool that you should have in your musical arsenal.
How Electronic Instruments Have Shaped EDM
The Influence of Technology on EDM
The Role of Early Electronic Instruments
The influence of technology on EDM can be traced back to the early days of electronic music. The invention of the first electronic instruments, such as the theremin and the synthesizer, paved the way for a new era of music production. These instruments allowed musicians to create entirely new sounds and textures, pushing the boundaries of what was possible in music.
The Rise of Digital Technology
The rise of digital technology in the late 20th century had a profound impact on EDM. The development of digital audio workstations (DAWs) and music software made it possible for producers to create and record music in a digital format. This revolutionized the music industry, making it easier and more affordable for producers to create and record their music.
The Evolution of Electronic Instruments
As technology has advanced, so too have the electronic instruments used in EDM. Today, producers have access to a wide range of electronic instruments, including virtual synthesizers, drum machines, and samplers. These instruments offer a level of versatility and creativity that was previously unimaginable, allowing producers to craft intricate and complex tracks with ease.
The Impact of Technology on Live Performance
Technology has also had a significant impact on live performance in EDM. The use of laptops and digital controllers has revolutionized the way DJs and producers perform live. Today, it is common for producers to incorporate live elements, such as vocals and instrumentation, into their performances, using technology to manipulate and transform these elements in real-time.
The Future of Technology in EDM
As technology continues to evolve, it is likely that it will play an increasingly important role in the world of EDM. With the rise of virtual reality and artificial intelligence, it is possible that we will see entirely new forms of electronic music emerge in the future. Only time will tell what the future holds for EDM and technology, but one thing is certain: the relationship between the two will continue to shape and define the music industry for years to come.
The Impact of Electronic Instruments on Music Production
The introduction of electronic instruments has significantly impacted the production of electronic dance music (EDM). These instruments have revolutionized the way music is created, recorded, and produced, providing musicians and producers with a vast array of sonic possibilities. In this section, we will explore the impact of electronic instruments on music production in EDM.
Electronic instruments have enabled producers to create complex and intricate sounds that were previously impossible to achieve with traditional acoustic instruments. With the use of synthesizers, for example, producers can create a wide range of timbres and textures, from bright and airy to dark and menacing. This has opened up new possibilities for musical expression and has allowed producers to push the boundaries of what is possible in music production.
Another significant impact of electronic instruments on music production is the ability to manipulate and edit sounds in ways that were previously impossible. Digital audio workstations (DAWs) have made it possible for producers to easily manipulate and edit sound files, allowing for precise control over every aspect of a track. This has enabled producers to create intricate and layered soundscapes, as well as to experiment with new and innovative sounds.
Furthermore, electronic instruments have made it possible for producers to collaborate and share their work with others in ways that were previously difficult or impossible. The internet has facilitated the sharing of music production techniques and resources, allowing producers to connect with other musicians and producers from around the world. This has led to a rapid exchange of ideas and techniques, and has helped to fuel the growth and evolution of EDM.
In addition, electronic instruments have enabled producers to create music that is more flexible and adaptable to different contexts. With the ability to easily manipulate and edit sound files, producers can create music that is tailored to specific events or environments. This has led to the development of new genres and subgenres of EDM, each with its own unique characteristics and stylistic elements.
Overall, the impact of electronic instruments on music production in EDM has been profound and far-reaching. These instruments have enabled producers to create new and innovative sounds, collaborate and share their work with others, and create music that is more flexible and adaptable to different contexts. As a result, EDM continues to evolve and grow, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in music production.
The Evolution of EDM Subgenres
Electronic Dance Music (EDM) has undergone a remarkable evolution since its inception in the 1970s. Over the years, the genre has diversified into numerous subgenres, each with its distinct characteristics and instruments. In this section, we will explore the evolution of EDM subgenres and the role that electronic instruments have played in shaping them.
One of the earliest subgenres of EDM was Detroit techno, which emerged in the early 1980s. This subgenre was characterized by its use of synthesizers and drum machines, which were used to create repetitive, mechanical beats. The sounds produced by these instruments were often harsh and industrial, reflecting the urban landscape of Detroit.
Another significant subgenre of EDM is house music, which originated in Chicago in the mid-1980s. House music was characterized by its use of 4/4 beats and simple, repetitive melodies. The genre relied heavily on synthesizers and drum machines to create its distinct sound, with many producers using Roland’s TR-808 and TR-909 drum machines to create the signature “boom-boom-boom” sound.
In the early 1990s, a new subgenre of EDM emerged, known as hardstep or hardstep techno. This subgenre was characterized by its use of aggressive, distorted basslines and heavily distorted synthesizers. Hardstep producers often used analog synthesizers such as the Roland TB-303 and Moog to create their sounds, which were influenced by the industrial and techno subgenres.
As EDM continued to evolve, new subgenres emerged, each with its unique sound and instruments. For example, the subgenre of dubstep, which emerged in the mid-2000s, relied heavily on the use of digital audio workstations (DAWs) and software synthesizers to create its distinctive “wobble” bass sound. Similarly, the subgenre of future bass, which emerged in the late 2000s, relied heavily on the use of virtual instruments and samples to create its ethereal, dreamy sound.
Overall, the evolution of EDM subgenres has been closely tied to the development of electronic instruments and technology. As new instruments and tools have become available, producers have been able to experiment with new sounds and styles, leading to the creation of new subgenres and the continued evolution of EDM.
Exploring the Different Sounds of EDM
House Music
House music is one of the most popular subgenres of electronic dance music (EDM). It originated in the 1980s in Chicago, and since then, it has evolved into a global phenomenon. House music is characterized by its four-on-the-floor beat, which is created by a kick drum hit on every first beat of a measure. This rhythm forms the foundation of the genre and provides a steady pulse that drives the music forward.
The instrumentation used in house music varies depending on the subgenre and the specific track. However, some of the most common instruments used in house music include:
- S synthesizer: The S synth is a software synthesizer that is widely used in house music production. It is known for its ability to create rich, complex sounds that are perfect for layering with other instruments.
- Electric guitar: While the electric guitar is not a traditional instrument in house music, it is often used to add a rock edge to the genre. Its distorted sound can create a gritty texture that adds depth to the music.
- Bass guitar: The bass guitar is a crucial instrument in house music, providing the low-end frequencies that drive the rhythm. A well-crafted bassline can make or break a track, and many house music producers spend hours perfecting their basslines.
- Drum machine: The drum machine is the backbone of house music, providing the rhythm that drives the genre. From simple Roland TR-808 kits to more complex patterns, the drum machine is an essential tool for any house music producer.
- Vocoder: The vocoder is an electronic instrument that is used to create vocal sounds. It is often used in house music to create robotic or alien-like sounds that add a futuristic element to the music.
In addition to these instruments, house music producers also use a variety of effects and processing techniques to create the unique sounds that define the genre. From distortion and reverb to filtering and delay, these effects can transform a simple melody or bassline into a complex and dynamic musical texture.
Overall, house music is a diverse and evolving genre that continues to push the boundaries of electronic music. With its driving rhythms and complex sounds, it is no wonder that house music has become one of the most popular subgenres of EDM.
Techno
Techno is a subgenre of electronic dance music that emerged in Detroit, Michigan during the mid-1980s. It is characterized by its repetitive, mechanical beats and futuristic sounds. The instruments used in techno music are largely electronic, with a focus on synthesizers and drum machines.
One of the most commonly used instruments in techno music is the Roland TR-808 drum machine. This machine was first released in 1980 and has since become a staple in the techno genre. Its distinctive, futuristic sounds have been used in countless techno tracks, including classic tracks like “Rise” by Azekel and “The Humdrum Revelation” by Underworld.
Another instrument commonly used in techno music is the Roland TB-303 bass synthesizer. This instrument was first released in 1981 and has a distinctive, squelchy sound that is often used in techno music. It was famously used in the creation of the sound of the “acid” in acid house, which is a subgenre of techno.
In addition to these instruments, many techno producers also use a variety of other synthesizers, effects units, and software to create their music. These can include virtual instruments, samplers, and drum machines, as well as more unconventional instruments like the Theremin or the Chapman Stick.
Overall, the instruments used in techno music are chosen for their ability to create futuristic, mechanical sounds that are often reminiscent of science fiction movies or futuristic video games. By using these instruments, techno producers are able to create a unique, otherworldly sound that has become synonymous with the genre.
Trance
Trance is a subgenre of electronic dance music that emerged in the early 1990s. It is characterized by a fast tempo, often between 125 and 150 beats per minute, and a emphasis on melodic elements and repetitive patterns.
Some of the key characteristics of trance music include:
- A strong emphasis on melody, often created using synthesizers and digital instruments
- Repetitive, hypnotic patterns known as “progressions”
- A strong emphasis on the “build up” and “drop” of the music, where the music gradually builds in intensity before dropping back down to a lower intensity
- The use of effects such as reverb and delay to create a sense of space and depth
Trance music is often produced using a combination of hardware and software instruments, such as synthesizers, drum machines, and digital audio workstations. Some of the most popular instruments used in trance production include:
- Synthesizers: trance producers often use a variety of synthesizers, such as virtual analog synthesizers, FM synthesizers, and wavetable synthesizers, to create the melodic and bass parts of their tracks.
- Drum machines: trance producers often use drum machines to create the rhythmic foundation of their tracks. These can include classic hardware drum machines, such as the Roland TR-808 and TR-909, as well as software-based drum samplers.
- Digital audio workstations (DAWs): trance producers often use DAWs, such as Ableton Live and Logic Pro, to create, record, and edit their tracks. These software tools allow producers to arrange and manipulate sound in a variety of ways, including layering, filtering, and effecting.
Overall, trance music is characterized by its fast tempo, emphasis on melody, and repetitive patterns. It is produced using a combination of hardware and software instruments, and can be created using a variety of different techniques and approaches.
Dubstep
Dubstep is a genre of electronic dance music that originated in the UK in the late 1990s. It is characterized by its heavy basslines, wobbles, and syncopated rhythms. The instruments used in dubstep production include:
- Saw Synth: This is a synthesizer that generates a sawtooth waveform, which is a fundamental sound in dubstep. The sawtooth waveform is created by drawing a continuous saw-like shape on an oscilloscope. The saw synth is used to create the bassline, which is the most prominent sound in dubstep.
- Sub-Bass: The sub-bass is a low-frequency sound that is used to create the foundation of the beat in dubstep. It is usually created using a synthesizer or a sampler, and is used to add weight and depth to the sound.
- Drum Samples: Dubstep producers use a variety of drum samples, including breakbeats, hardstep, and techstep. These samples are manipulated and processed to create the distinctive rhythms of dubstep.
- FX: Effects are an essential part of dubstep production. Reverb, delay, and distortion are used to create a sense of space and movement in the sound. Filters are also used to manipulate the frequency range of the sounds, creating a sense of depth and dimension.
In addition to these instruments, dubstep producers also use a variety of software and hardware to create their music. Digital audio workstations (DAWs) are used to record, edit, and arrange the sounds, while analog synthesizers and effect units are used to create unique and unconventional sounds.
Famous EDM Artists and Their Instrumentation
The Rise of DJs
In the world of electronic dance music, DJs have become an integral part of the industry. Their rise to prominence can be attributed to several factors, including the proliferation of music technology, the growth of the nightlife scene, and the demand for live performances.
The Proliferation of Music Technology
The widespread availability of affordable and user-friendly music technology has played a significant role in the rise of DJs. With the advent of digital audio workstations (DAWs) and other music production software, aspiring DJs can now produce and record their own tracks from the comfort of their homes. This has democratized the music industry, enabling DJs to gain a foothold in the market without the need for expensive equipment or extensive musical training.
The Growth of the Nightlife Scene
Another factor contributing to the rise of DJs is the growth of the nightlife scene. As cities around the world have become more cosmopolitan, the demand for entertainment venues has increased. This has created a market for DJs, who can provide the soundtracks for parties, clubs, and other social events. The popularity of electronic dance music has also fueled this trend, as DJs are often the primary performers at EDM events.
The Demand for Live Performances
Finally, the demand for live performances has also played a role in the rise of DJs. As music has become more accessible through streaming services and other digital platforms, the experience of attending a live concert or festival has become more important to fans. DJs, with their ability to create a unique and immersive audio experience, have become an essential part of the live music scene. Their skill in curating and mixing tracks in real-time has made them sought-after performers at festivals and other events around the world.
Overall, the rise of DJs in the world of electronic dance music has been driven by a combination of technological advancements, changes in the nightlife scene, and the demand for live performances. As the industry continues to evolve, DJs will likely remain an integral part of the EDM landscape.
Notable EDM Producers and Their Work
The world of electronic dance music (EDM) has seen the rise of many talented producers who have made a significant impact on the genre. Here are some notable EDM producers and their work:
Skrillex
Sonny Moore, better known by his stage name Skrillex, is an American DJ and producer who rose to fame in the late 2000s. He is known for his unique sound that blends elements of dubstep, electro-house, and heavy metal. Some of his most popular tracks include “Bangarang,” “Reptile,” and “Scary Monsters and Nice Sprites.”
Deadmau5
Joel Zimmerman, aka Deadmau5, is a Canadian DJ and producer known for his iconic mouse-head helmet and his progressive house and techno music. Some of his most popular tracks include “Strobe,” “Ghosts ‘n’ Stuff,” and “I Remember.”
Daft Punk
Daft Punk is a French electronic music duo consisting of Thomas Bangalter and Guy-Manuel de Homem-Christo. They are known for their innovative use of technology and their influential contributions to the EDM scene. Some of their most popular tracks include “One More Time,” “Around the World,” and “Harder, Better, Faster, Stronger.”
The Chemical Brothers
The Chemical Brothers, consisting of Tom Rowlands and Ed Simons, are an English electronic music duo known for their energetic live performances and their fusion of various musical genres. Some of their most popular tracks include “Go,” “Block Rockin’ Beats,” and “Parklife.”
These are just a few examples of the many talented EDM producers who have made a significant impact on the genre. Each producer has their own unique style and approach to music production, making EDM a diverse and constantly evolving genre.
The Role of Collaboration in EDM
In the world of Electronic Dance Music (EDM), collaboration plays a crucial role in the creation of new sounds and innovative tracks. Collaboration involves two or more artists coming together to create a musical work, sharing their skills, ideas, and knowledge to produce a unique sound. In EDM, collaboration can take many forms, from working together in the studio to sharing tracks online through platforms like SoundCloud.
Collaboration in EDM can lead to some of the most groundbreaking and exciting music. When artists from different backgrounds and genres come together, they bring with them their own unique styles and sounds, which can lead to a fusion of different musical elements. This fusion can create a new sound that would not have been possible without collaboration.
Collaboration also allows artists to push the boundaries of what is possible in EDM. When working with someone who has a different approach to music production, artists can learn new techniques and ideas that they may not have considered before. This can lead to a more diverse and innovative sound, as well as a greater understanding of the creative process.
In addition to the creative benefits of collaboration, it can also help to build relationships between artists and promote a sense of community within the EDM scene. Collaboration can lead to new friendships and partnerships, as well as opportunities for future projects and collaborations.
Overall, collaboration is a crucial aspect of EDM, allowing artists to push the boundaries of what is possible, create new sounds, and build relationships within the community. Whether it’s working together in the studio or sharing tracks online, collaboration is an essential part of the EDM scene.
The Future of Electronic Instruments in EDM
The Impact of Technological Advancements
As technology continues to advance, the world of electronic dance music (EDM) is evolving at a rapid pace. The integration of new technologies has had a profound impact on the instruments used in EDM, enabling producers to create more complex and intricate sounds than ever before. Here are some of the key ways in which technological advancements are shaping the future of electronic instruments in EDM.
- Virtual Instruments: With the rise of digital audio workstations (DAWs) and virtual instrument technology, it’s now possible for producers to create and manipulate a wide range of sounds using nothing more than a computer and a few software plugins. Virtual instruments allow for an almost infinite number of sonic possibilities, and they can be easily edited and manipulated to create unique and innovative sounds.
- MIDI Controllers: MIDI controllers have also played a major role in the evolution of electronic instruments in EDM. These devices allow producers to input notes and other MIDI data into their DAWs, enabling them to create complex and dynamic arrangements with ease. MIDI controllers come in a variety of shapes and sizes, from small and portable devices to large and complex systems with multiple buttons, knobs, and faders.
- Sampling and Sound Design: Sampling and sound design are also crucial elements of EDM production, and they have been greatly enhanced by technological advancements. With access to vast libraries of sounds and samples, producers can easily incorporate a wide range of sonic elements into their tracks. They can also use software tools to manipulate and transform these sounds, creating entirely new textures and timbres.
- Hardware Synthesizers: While virtual instruments and software plugins have revolutionized the world of EDM production, many producers still prefer to work with hardware synthesizers. These devices offer a tactile and intuitive interface for creating and manipulating sounds, and they can be used to generate a wide range of tones and textures. As technology continues to advance, hardware synthesizers are becoming more sophisticated and versatile, offering producers new ways to explore the possibilities of electronic sound creation.
Overall, the impact of technological advancements on the world of EDM cannot be overstated. From virtual instruments to MIDI controllers, sampling and sound design to hardware synthesizers, these technologies are enabling producers to create a wider range of sounds than ever before, pushing the boundaries of electronic music and opening up new avenues for artistic expression.
The Role of Virtual Instruments
The role of virtual instruments in electronic dance music (EDM) is rapidly increasing. These instruments are digital replicas of traditional acoustic instruments or synthesizers that can be used to create and manipulate sound. They are often used in the production of EDM due to their versatility and ability to create a wide range of sounds.
One of the main advantages of virtual instruments is their portability. Unlike traditional instruments, virtual instruments can be easily stored and accessed on a computer or mobile device. This allows producers to create music from anywhere and at any time.
Another advantage of virtual instruments is their ability to be edited and manipulated in real-time. This allows producers to experiment with different sounds and effects, creating unique and dynamic music.
Virtual instruments also offer a wide range of sound options. Many virtual instruments come with pre-programmed sounds, but they can also be edited and customized to create new sounds. This allows producers to experiment with different sonic textures and create music that stands out from the crowd.
Overall, the role of virtual instruments in EDM is likely to continue to grow in the future. Their versatility, portability, and ability to create unique sounds make them an essential tool for producers looking to create cutting-edge music.
The Evolution of AI-Generated Music
The role of artificial intelligence (AI) in music production has been steadily increasing over the past few years. AI algorithms can now be used to generate music in a variety of styles, from classical to electronic dance music (EDM).
One of the most exciting developments in AI-generated music is the ability to create music that sounds like it was composed by a human. This is known as “AI-generated music” or “AI-composed music.”
One of the most well-known AI-generated music projects is Amper Music, which uses AI algorithms to compose custom music for videos. The music is generated based on the characteristics of the video, such as its genre, mood, and tempo.
Another example of AI-generated music is the AI Music Lab, which allows users to create music using a simple interface. The user can choose from a variety of styles and instruments, and the AI algorithm will generate a unique piece of music based on the user’s selections.
In the future, it is likely that AI-generated music will become even more sophisticated, allowing for greater creativity and personalization in music production. It is also possible that AI algorithms will be used to create entirely new styles of music that have never been heard before.
Overall, the evolution of AI-generated music is an exciting development for the future of electronic instruments in EDM. As AI algorithms become more advanced, they will open up new possibilities for music production and enable musicians and producers to create even more unique and innovative sounds.
The Enduring Appeal of Electronic Dance Music
The popularity of electronic dance music (EDM) has exploded in recent years, and it shows no signs of slowing down. EDM has become a staple of the modern music industry, and its enduring appeal can be attributed to several factors.
One reason for the enduring appeal of EDM is its versatility. EDM encompasses a wide range of styles, from the energetic beats of techno and house music to the soulful melodies of trance and deep house. This versatility allows EDM to appeal to a broad audience, from club-goers to festival-goers to music enthusiasts of all ages.
Another reason for the enduring appeal of EDM is its ability to innovate and evolve. As technology advances, new electronic instruments and production techniques are developed, allowing EDM producers to push the boundaries of what is possible in music. This constant innovation keeps EDM fresh and exciting, ensuring that it remains relevant to audiences today and in the future.
Finally, the enduring appeal of EDM can be attributed to its ability to connect people across cultures and boundaries. EDM has a universal language that transcends nationality, race, and age. It brings people together in a shared experience of music, dancing, and community. This universal appeal of EDM has made it a beloved genre around the world, with fans in every corner of the globe.
Overall, the enduring appeal of EDM is a testament to its power as a musical genre. Its versatility, innovation, and universal appeal make it a force to be reckoned with in the music industry, and its popularity is sure to continue for years to come.
The Importance of Continuous Innovation in Music Production
Electronic Dance Music (EDM) has come a long way since its inception in the 1970s. Today, it is a global phenomenon that spans across genres, cultures, and continents. The continuous evolution of technology has played a significant role in the development of EDM, enabling producers to experiment with new sounds, textures, and techniques.
One of the most critical factors that have contributed to the success of EDM is the constant pursuit of innovation. Producers and artists are always on the lookout for new ways to push the boundaries of what is possible with electronic instruments. This drive for innovation has led to the creation of new sounds, techniques, and technologies that have revolutionized the music industry.
Innovation in music production is not just about creating new sounds or effects. It is also about finding new ways to express emotions, tell stories, and connect with audiences. By continuously pushing the limits of what is possible with electronic instruments, producers can create music that is unique, original, and emotionally engaging.
However, innovation in music production is not without its challenges. Producers must constantly adapt to new technologies, software, and hardware, which can be time-consuming and expensive. They must also balance the need for innovation with the need for accessibility, ensuring that their music is accessible to a wide range of audiences.
Despite these challenges, the importance of continuous innovation in music production cannot be overstated. It is what sets EDM apart from other genres and keeps it relevant in an ever-changing musical landscape. By embracing new technologies, techniques, and ideas, producers can create music that is both timeless and timely, resonating with audiences across generations and cultures.
In conclusion, the importance of continuous innovation in music production cannot be overlooked. It is what drives the evolution of EDM and keeps it at the forefront of the music industry. Producers who embrace innovation and experimentation will be better equipped to create music that is fresh, exciting, and inspiring, capturing the imagination of audiences around the world.
The Future of EDM and Its Instruments
Electronic Dance Music (EDM) has come a long way since its inception in the 1970s. Today, it is a global phenomenon that continues to evolve and push the boundaries of music production. With the advancement of technology, the future of EDM and its instruments is looking brighter than ever.
One of the biggest changes in the future of EDM is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into music production. AI can help create new sounds, identify patterns, and even generate entire tracks. This technology is already being used by some of the biggest names in the industry, and it is expected to become even more prevalent in the future.
Another area where EDM is expected to make significant strides is in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) experiences. With VR and AR, fans can experience EDM in a whole new way, with immersive visuals and audio that transport them to another world. This technology is already being used in some EDM festivals, and it is expected to become even more popular in the future.
The future of EDM also involves the use of more sustainable and eco-friendly instruments. As the world becomes more conscious of its environmental impact, musicians and producers are looking for ways to reduce their carbon footprint. This means exploring new materials and technologies that are more environmentally friendly, such as solar-powered instruments and sustainable synthesizers.
In addition to these technological advancements, the future of EDM also involves a greater focus on mental health and wellness. As the music industry becomes more competitive and stressful, many producers and DJs are struggling with mental health issues. To address this, some EDM communities are organizing events and workshops that focus on mindfulness, meditation, and other practices that promote mental health and wellness.
Overall, the future of EDM and its instruments is bright and full of possibilities. With advancements in technology, sustainability, and mental health, EDM is poised to continue its evolution and shape the future of music production.
FAQs
1. What is EDM?
Electronic Dance Music (EDM) is a broad range of percussive electronic music genres produced largely for nightclubs, festivals, and raves. EDM is generally produced for playback by DJs who create seamless selections of tracks called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called a mix, called